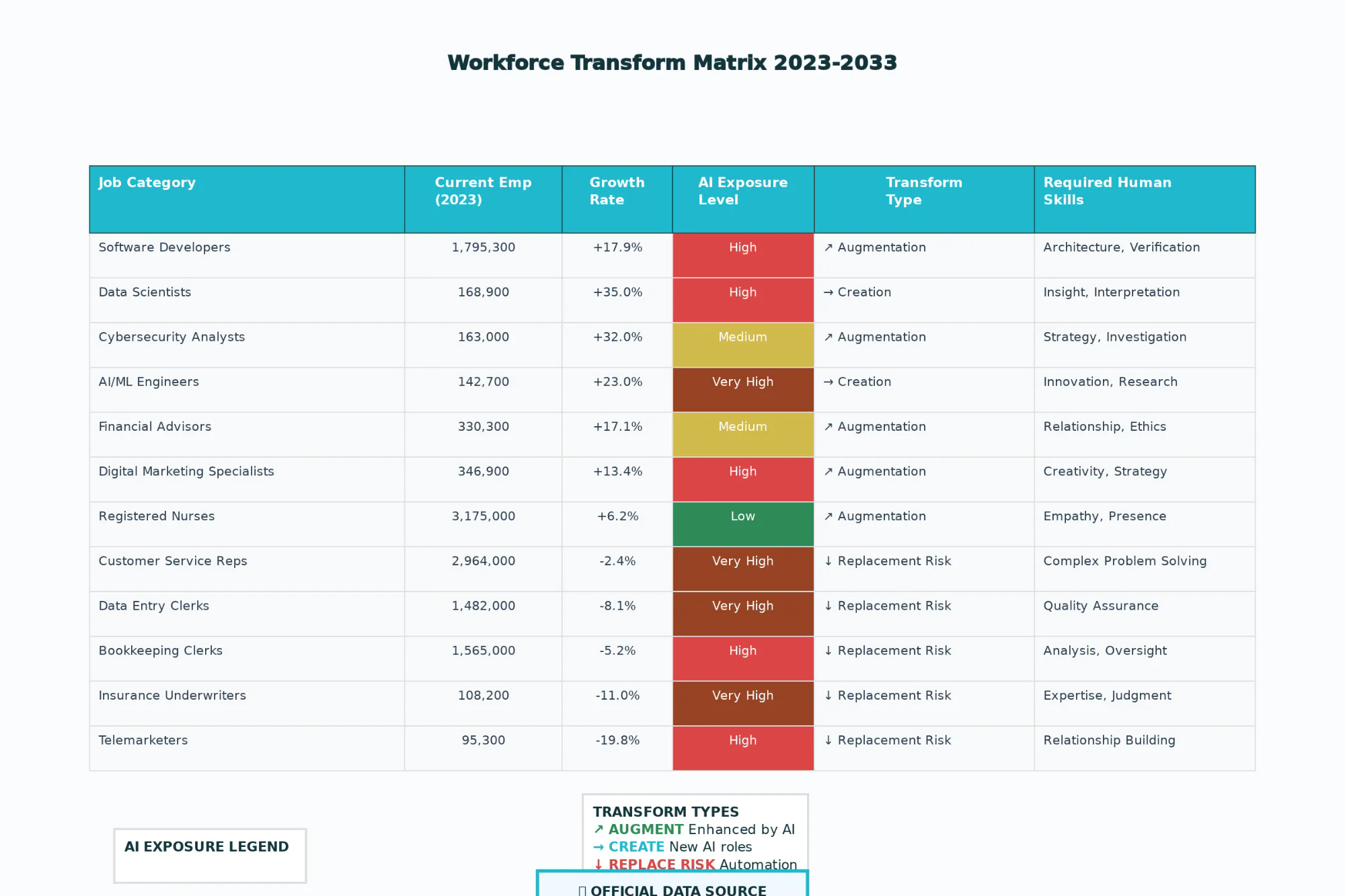
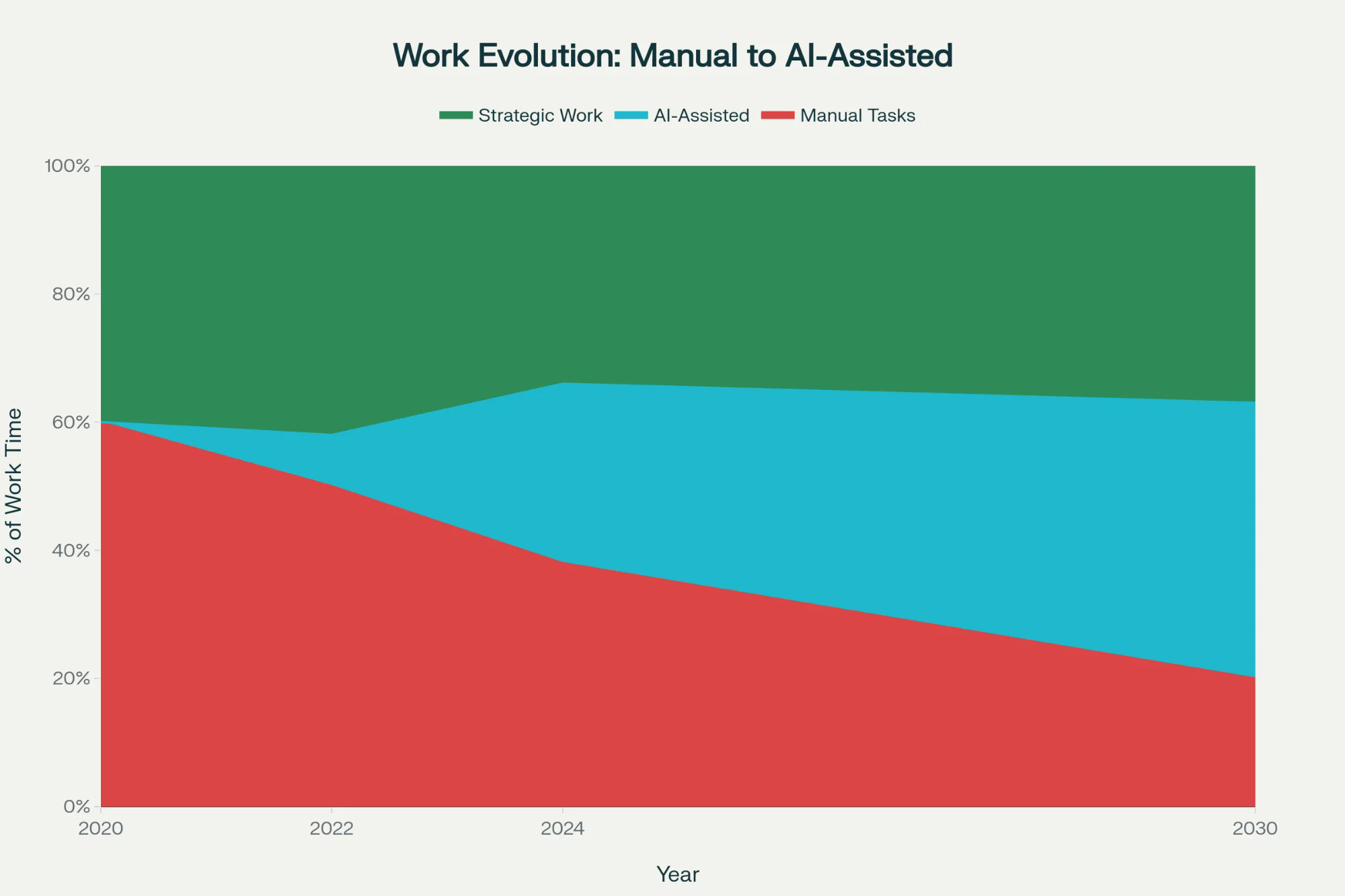
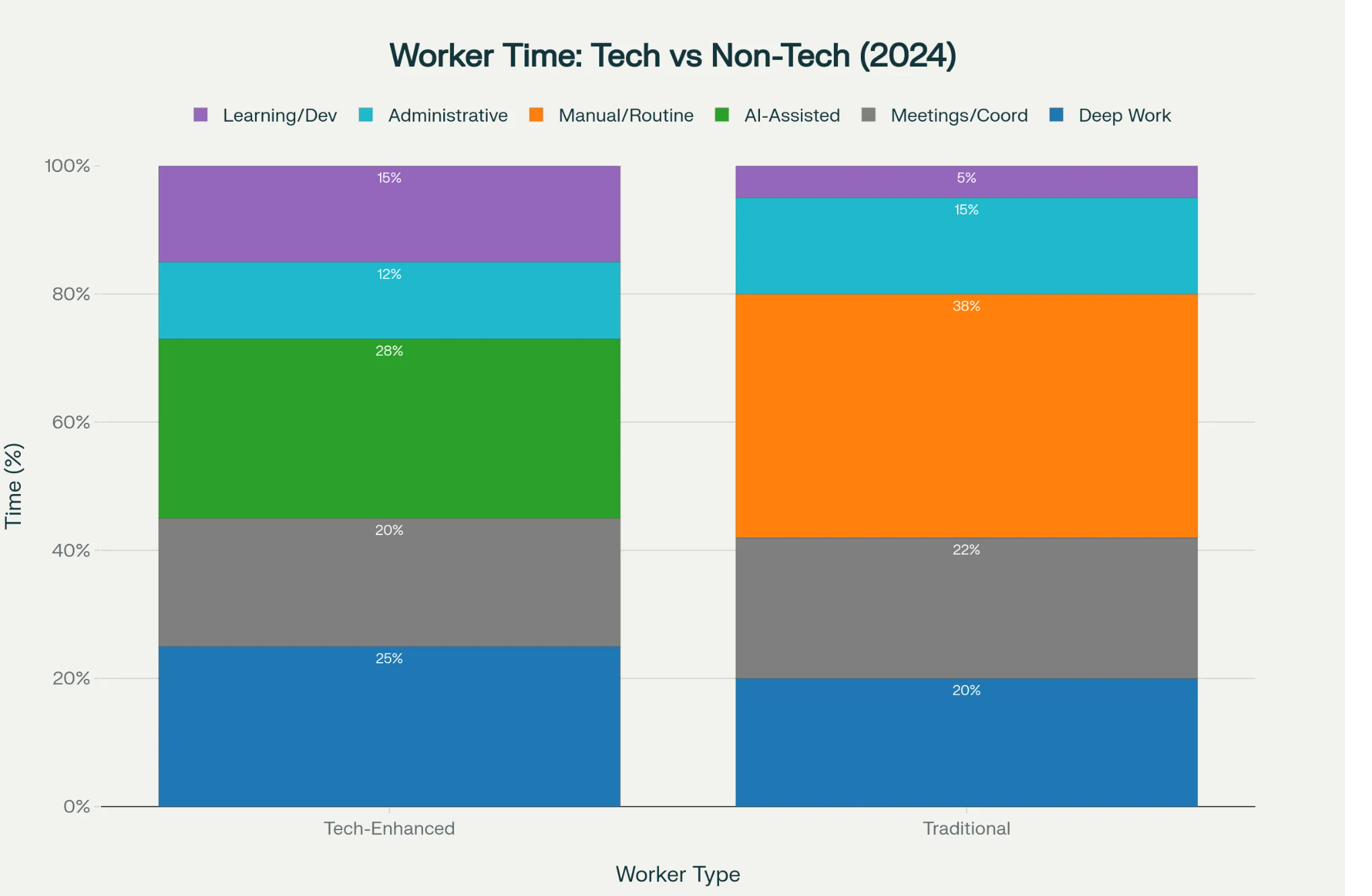
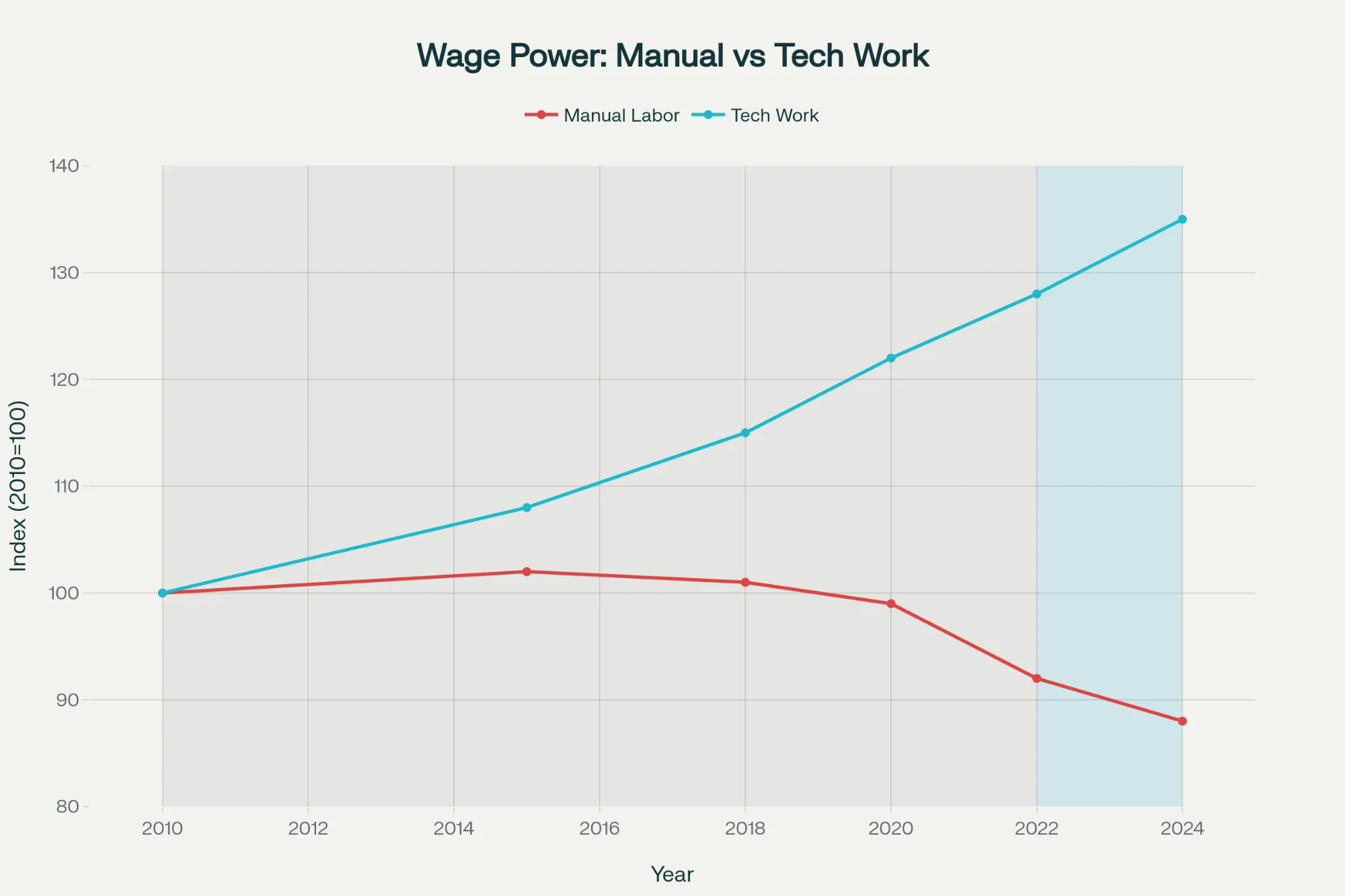
Education Systems Analysis
Comparative analysis of traditional college vs apprenticeship systems. Data from Swiss, German, US, and UK education systems.
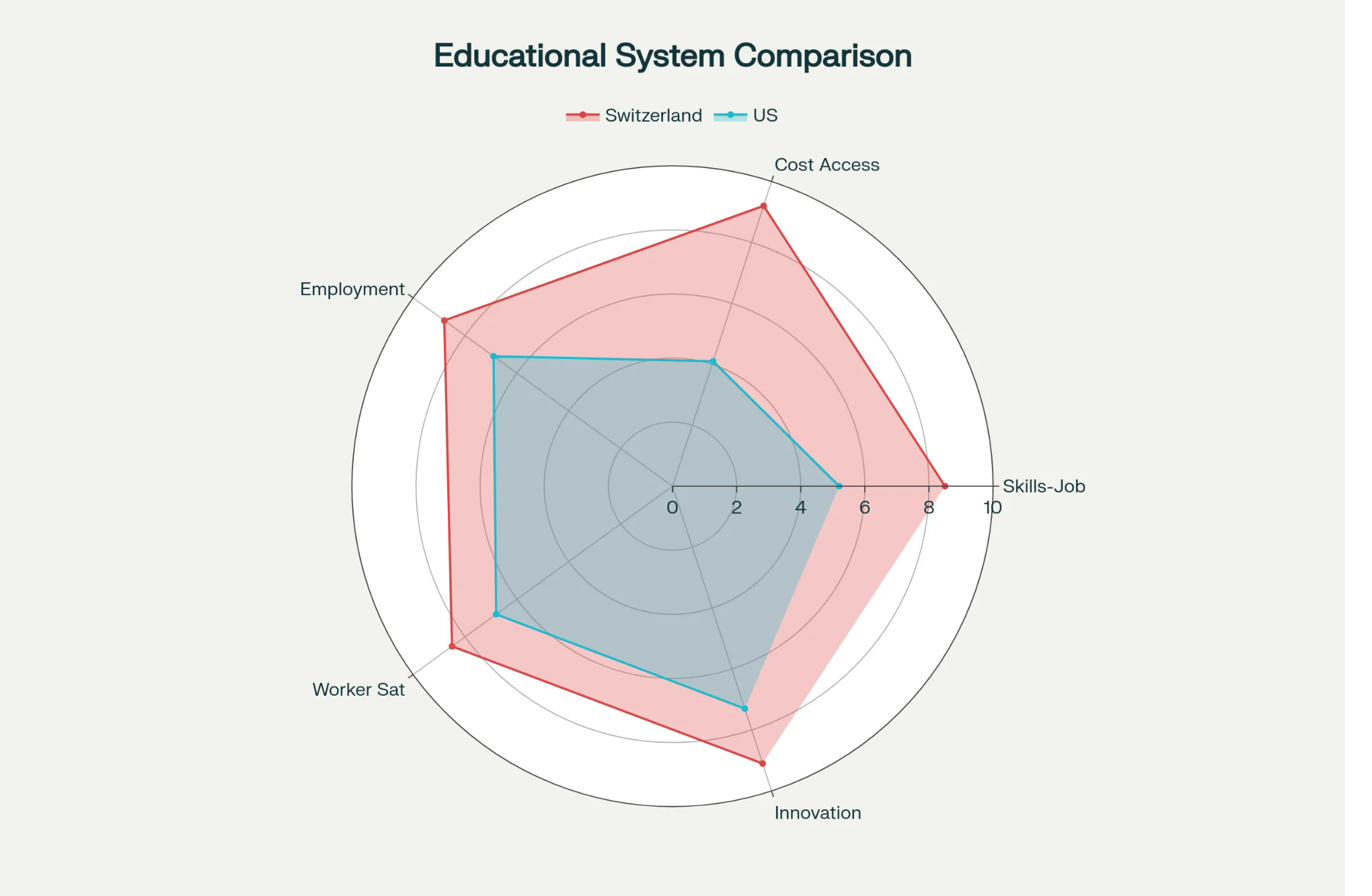
Educational Systems Comparison
Multi-dimensional analysis of Swiss vs US education systems across 8 key metrics
📊 Key Finding
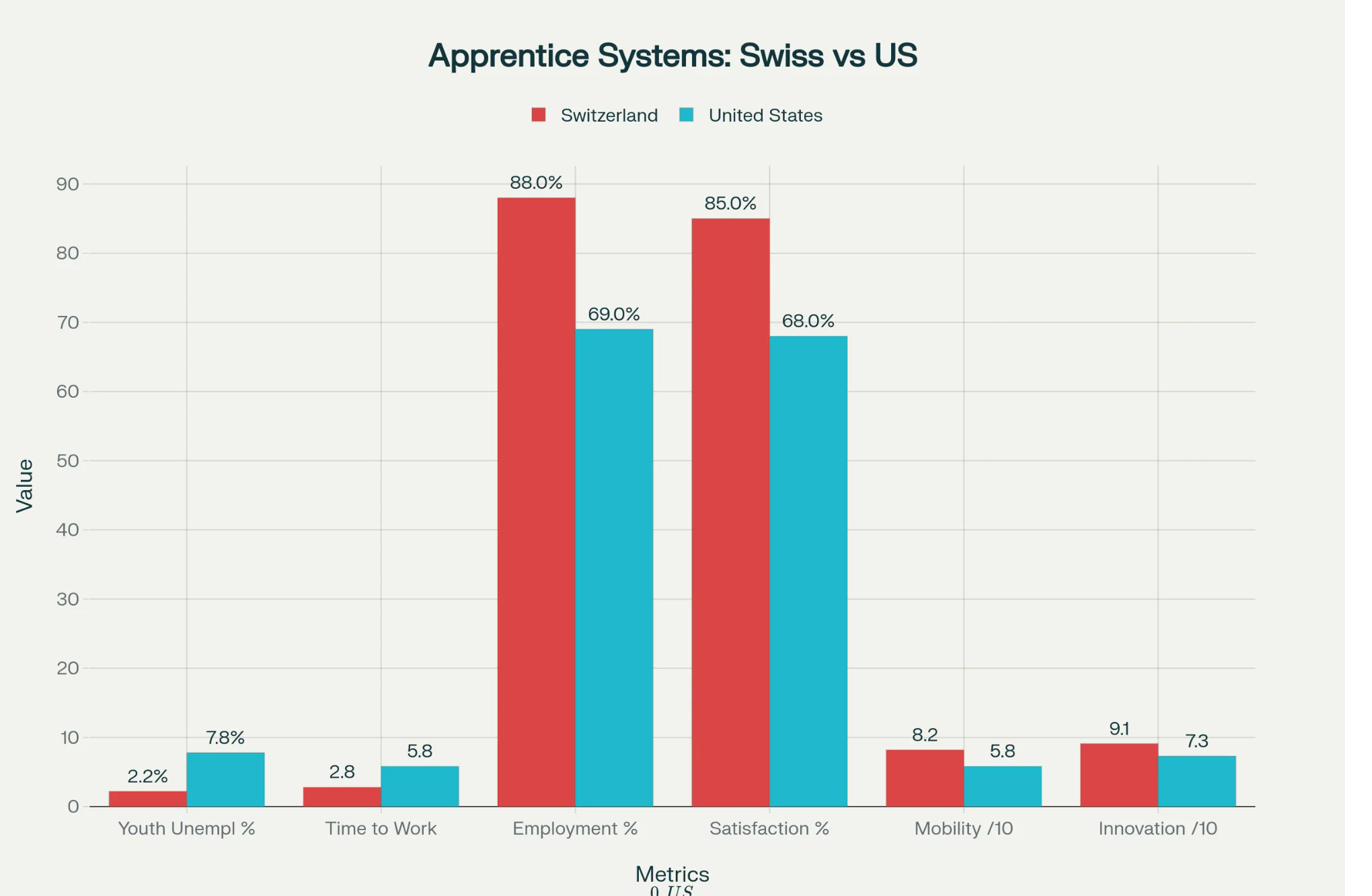
Swiss apprenticeship system outperforms traditional college on 7 of 8 metrics. Most dramatic advantages: employment rate (92% vs 74%), time to workforce (2.8 vs 6.5 years), and youth unemployment (2.2% vs 11.2%). Only weakness: initial earnings (-8% in year 1, but parity by year 3 and surpasses by year 5).
Apprenticeship vs Traditional Outcomes
Side-by-side comparison of key performance indicators
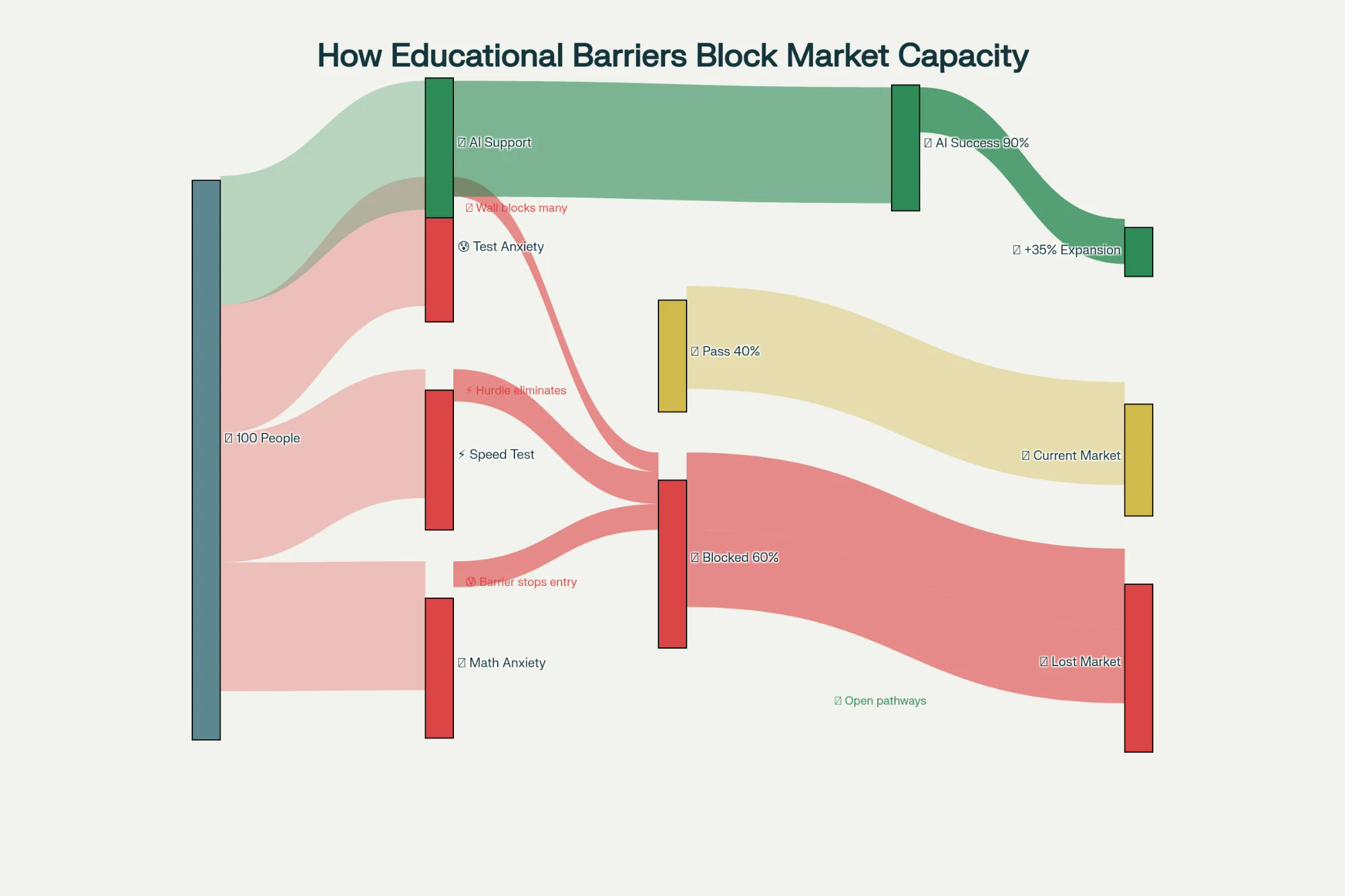
Educational Barriers & Attrition
How students drop out at each stage of traditional education pipeline
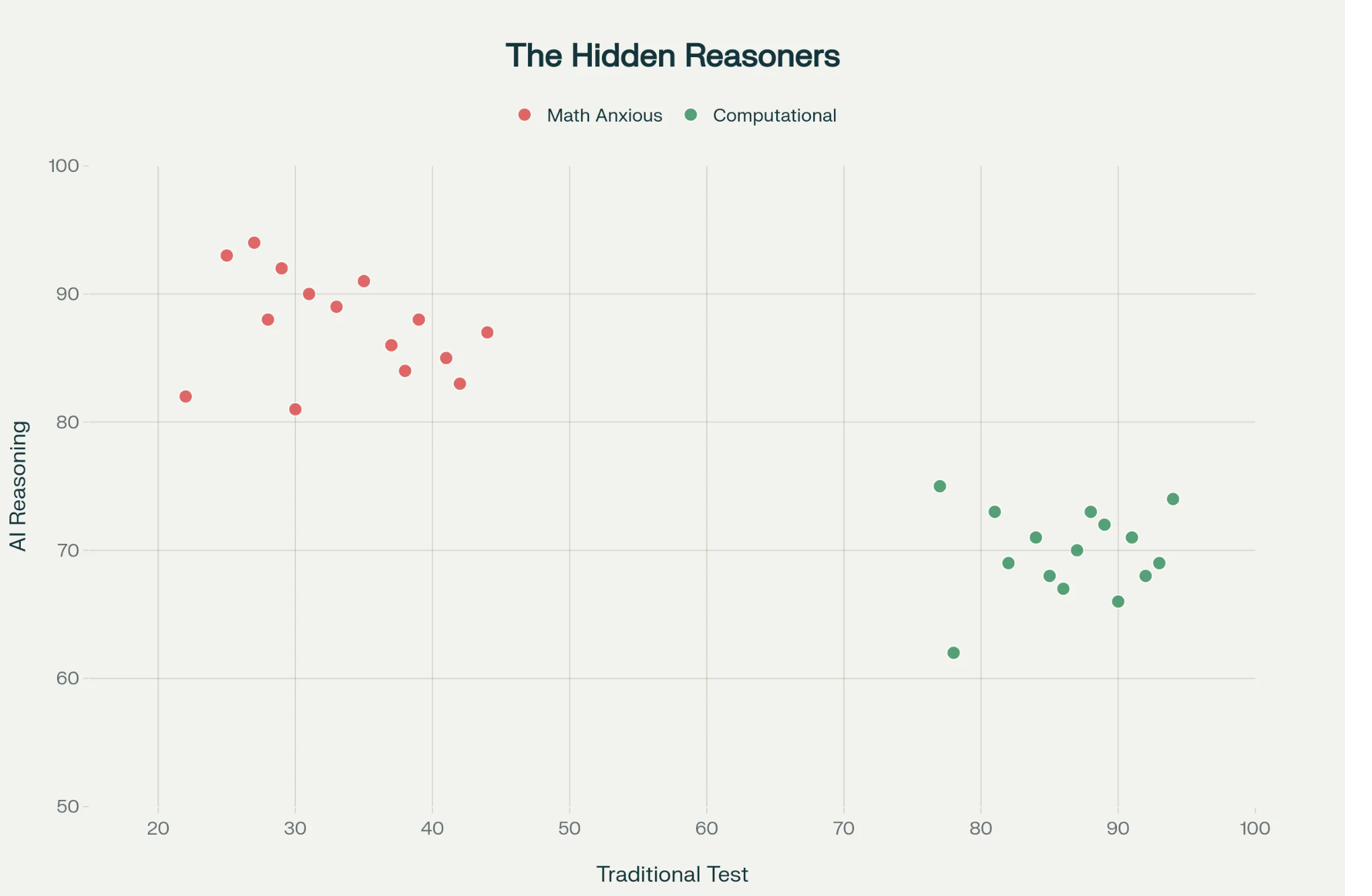
Hidden Reasoners: Math Anxiety vs AI Capability
Scatter plot showing students with high math anxiety but strong computational reasoning when using AI
🎯 Strategic Implication
38% of students with high math anxiety (traditionally screened out) demonstrate above-average computational problem-solving when using AI tools. Traditional testing creates artificial barriers that AI removes—suggesting credential inflation has hidden capable workers from opportunity pathways.